How networks form: Charting the developing brain
How can you build neuronal networks that are more complex than anything known today? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research in Frankfurt, Germany, have mapped the development of inhibitory neuronal circuitry and report the discovery of distinct circuit formation principles. Their findings enable scientists to monitor the change of neuronal network structure with time, capturing moments when an individual grows and adapts to its environment.
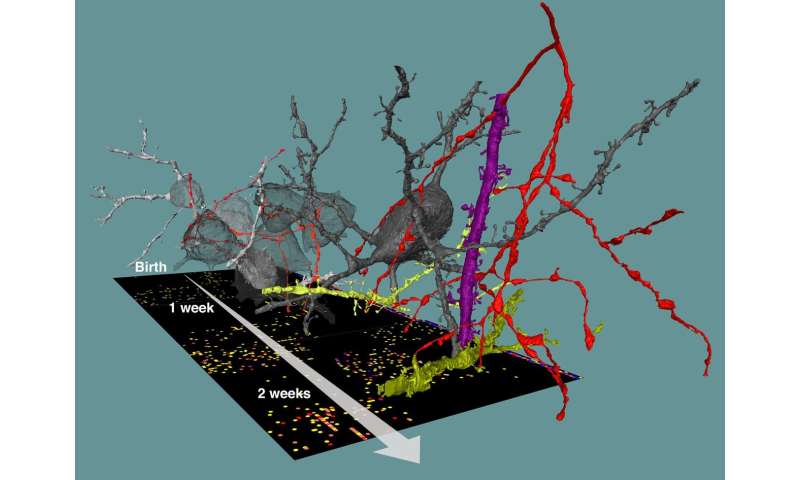
Researchers are starting to better understand the complexity of neuronal networks found in our and animals’ brains. But how can such precise and convoluted neuronal circuitry be built in the first place? We know how neurons are born, travel to their location in the gray matter, grow and differentiate. But how and by what rules do the trillions of synapses—the sophisticated contact points via which neurons “talk to teach other”—unfold, often at highly precise locations to form our brain’s networks? In the work published today in Science, a team around Max Planck Director Moritz Helmstaedter analyzed a total of thirteen 3-dimensional datasets from the cortex of mice during different stages of development: after birth, at time points comparable to baby, child, teenager and young adult. They used methods called “connectomics” to map out the neuronal circuitry found in the gray matter of the cerebral cortex, where most of the cerebral synapses are placed. By focusing on synapses of a type of nerve cells called interneurons, which are known to inhibit the activity of other neurons in highly specific ways, they were able to track the development of synaptic partner choice for these particular types of nerve cells.
“Surprisingly, different types of interneurons followed very different time courses to establish their favorite synaptic partners. Some were able to innervate their synaptic targets with adult-like preference already in the first investigated circuit stages that correspond to baby brains. This happened immediately when the first chemical synapses were formed in the cortical gray matter. Others showed steep improvements of target choice, which were most likely caused by removal of incorrectly placed synapses,” explains Anjali Gour, a Ph.D. student in the department and the first author of this study.
Studies had found before that in some parts of the brain, development not only involves the creation of new synapses but required the removal of synapses, as well. The finding that synapse removal (or pruning) has a precise and highly specific function for inhibitory circuit formation was, however, a major surprise. The researchers also found that a major class of interneurons, so-called Chandelier neurons, assumed to be fully established only in early adolescence, show much earlier and more systematic innervation of their synaptic partner structures than previously known.
These insights were possible in spite of the fact that the mapping of connectomes is a “snapshot” technique: neuronal networks can be measured in biopsies of brain tissue, but cannot be further followed over time in the same piece of brain. Rather, many measurements from different brains need to be made. “That we were able to still extract a clear developmental profile from this data illustrates the density of information present in connectomic data,” says Gour. “I would not have predicted that we would find such clear circuit patterns in brains that are still under development,” she adds.
The developmental processes of neuronal network formation and their possible disruption are thought to be major contributors to some of the main psychiatric disorders, and a particular focus of research has identified a contribution of inhibitory circuits to these dysfunctions. Hence, a precise and detailed understanding of inhibitory circuit is a prerequisite for targeted analysis and possible interference in such disease conditions. “We hope to be able to map much more precisely the normal and disrupted network formation in cortical circuits for understanding possible alterations in psychiatric disease, and possibly identify the phenotypes of connectopathies,” says Helmstaedter.
Source: Read Full Article


